Department News
Joint research team of prof Kim Ho-Young develop a soft gel actuators can break bricks
Author
익명
Date
2022-04-18
Views
1180
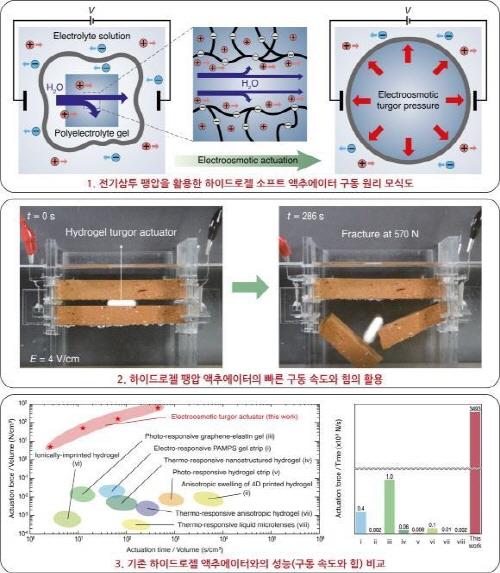
According to Seoul National University the April 15th, a research team led by Sun Jeong-Yun, a material engineering professor, and Kim Ho-young, a mechanical engineering professor, developed a soft gel actuator based the cell structure of plants. The soft gel actuator is a driving device that allows soft robots made of flexible materials, not hard metal, to move.the robot
It has been recognized that soft gel actuators are slow and weak, making them difficult to use for artificial muscles and biomimetic robots. The researchers noted that, when plant cells suck in water, pressure is strong enough to break the stone, but the cell walls endure the pressure.
The researchers explained that the output density is about 100,000 times greater than that of conventional gel-based actuators.The actuator developed this time is a structure in which a membrane that is permeable like a plant cell structure is wrapped around a hydrogel, and when the hydrogel expands by osmotic pressure in an underwater environment, 1g of the hydrogel can weigh 130kg without any external power source.
Even though this actuator does not need an external power source, but if an electric field is used as an external power source, it can generate more power at a faster speed by adding electric osmosis to the existing osmosis phenomenon. In this case, 1g of hydrogel can break bricks 2cm thick within 5 minutes. The actuator is expected to be used for floating buildings and undersea city construction.
Professor Sun Jeong-Yun predicted, "This study overcomes the fundamental limitations of soft gel actuators and will contribute to commercialization of artificial muscles, soft robotics, and biomedical engineering."
Meanwhile, the research results were published in "Science", the world's top international journal.
[Source: 연합뉴스, https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20220415069200004]

